Explanation
In recommender systems, the concept of control is associated with ways users can manipulate the system through interactions or by defining parameters in order to be provided more personal and better recommendations. Other studies in the movie domain have found that users may have a divergent perception of similarity regarding which features are important to them when looking for similar movies. This thesis sets out to investigate if these divergent opinions on similarity can be leveraged by controllability in the multi-lists presentation of recommendations. This thesis shows that user control did not appear to be evaluated more positively than a non-control recommender system for the average participant. This thesis found that multi lists presentation of recommendations without control were generally evaluated better than with control by performing a quantitative conditional user evaluation of the recommender system. When looking at participants’ demographic properties, it may be that some subgroups consisting of users with a higher level of domain knowledge or similar system experience may favor control. Furthermore, no significant variances between the three list sort methods that the system uses to enforce the users’ control were discovered. As controllability in recommender systems have not been extensively evaluated in the research corpus, this thesis hopes to be a starting point that can inspire future studies to attempt other novel approaches in implementing and evaluating controllability in the multi-lists presentation of recommendations to achieve more positive results.
Survey description
Detailed Explanation
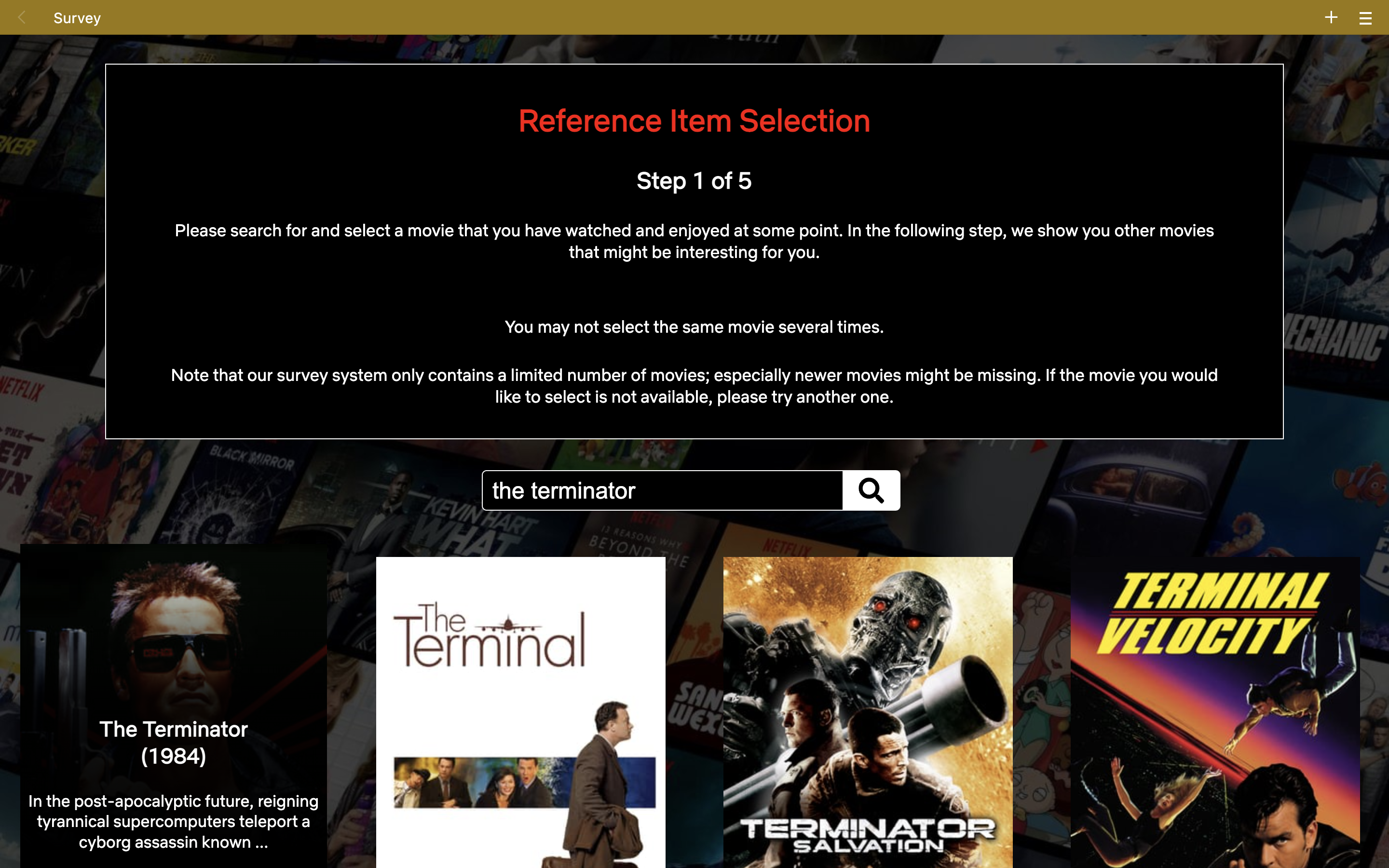
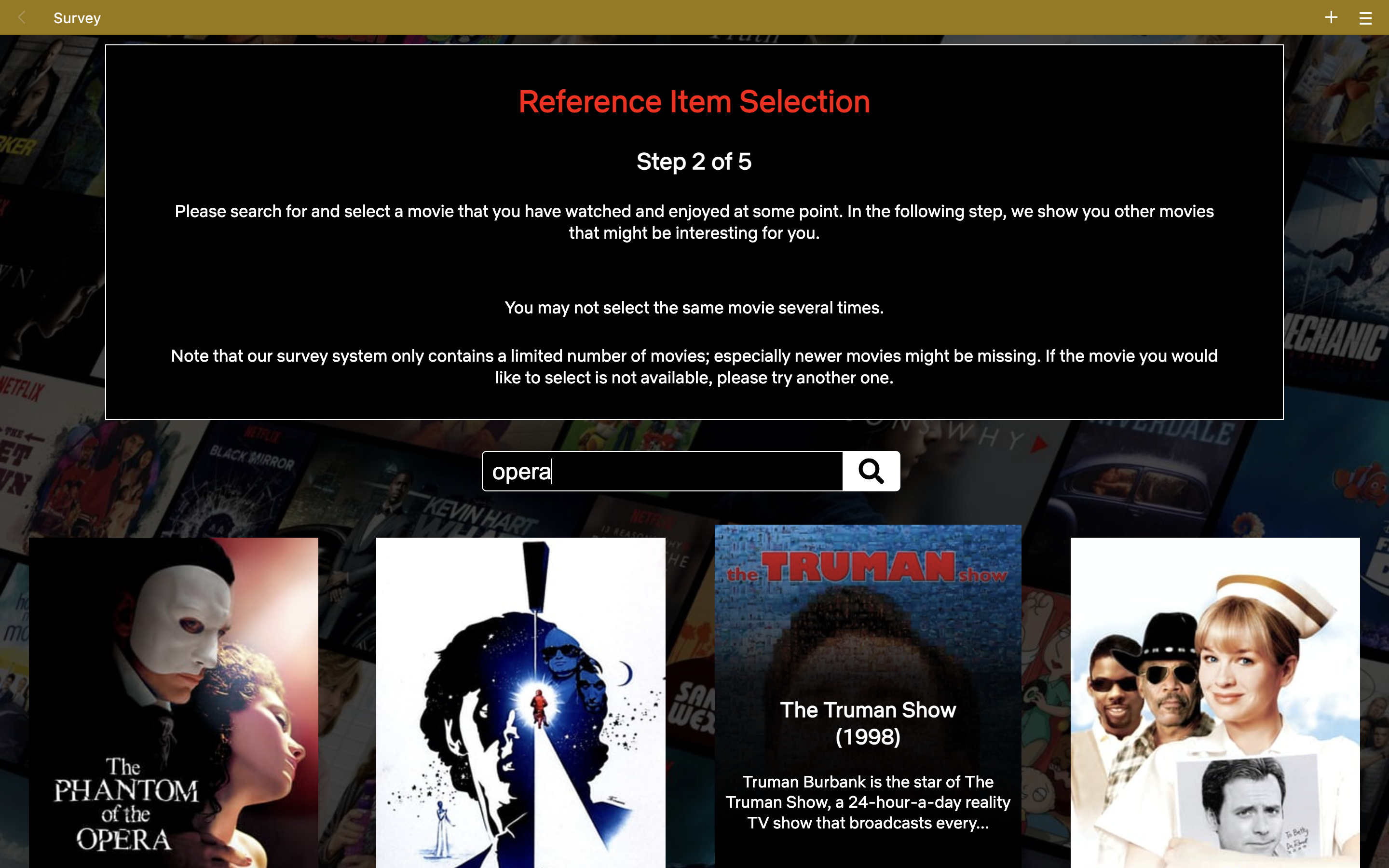
# Step One
A user is prompted to search for a reference movie.
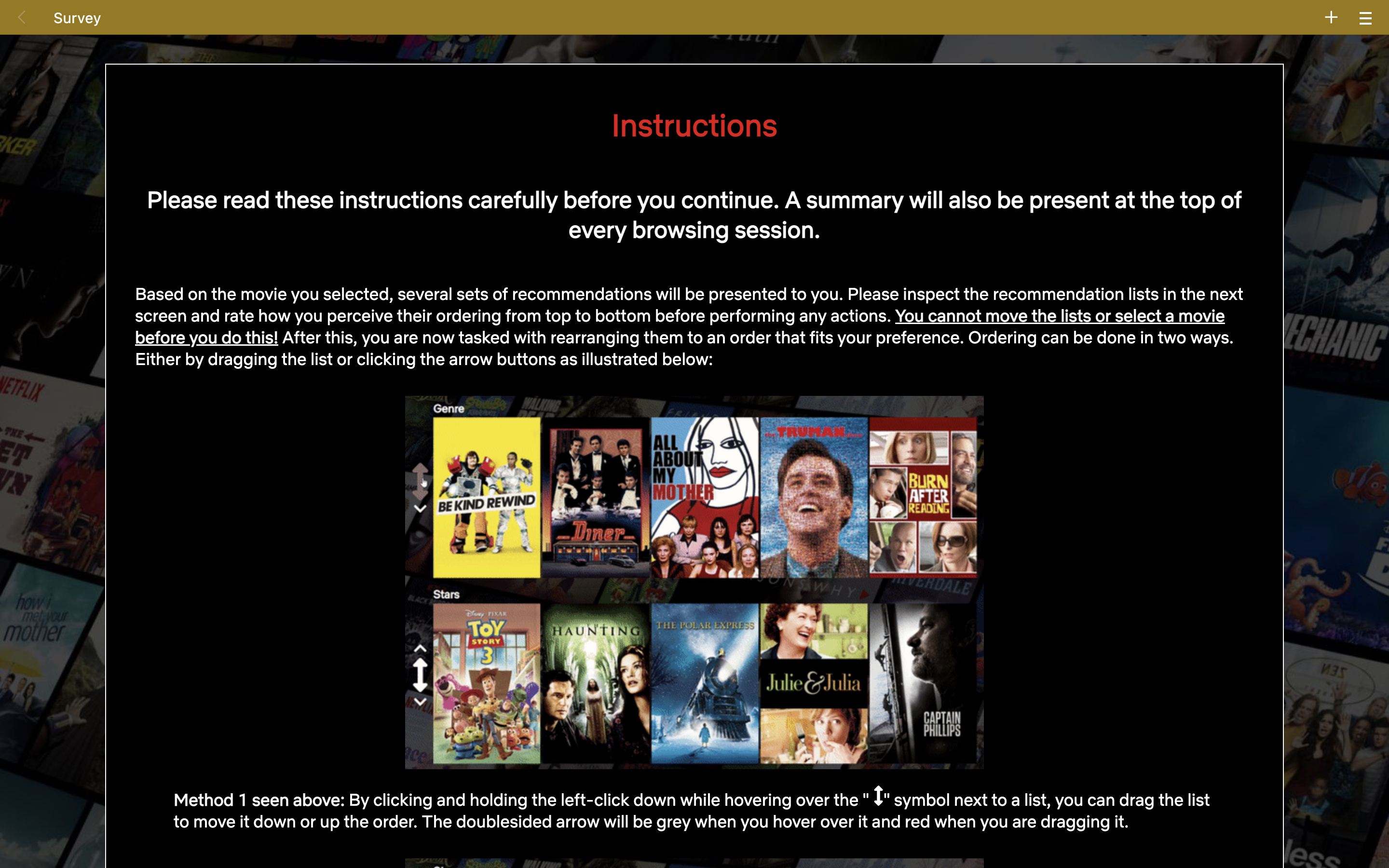
# Step Two
A user is instructed on how they can control the order of the recommendations.
# Step three
A user is asked to rate how satisfied they are with the current list order.
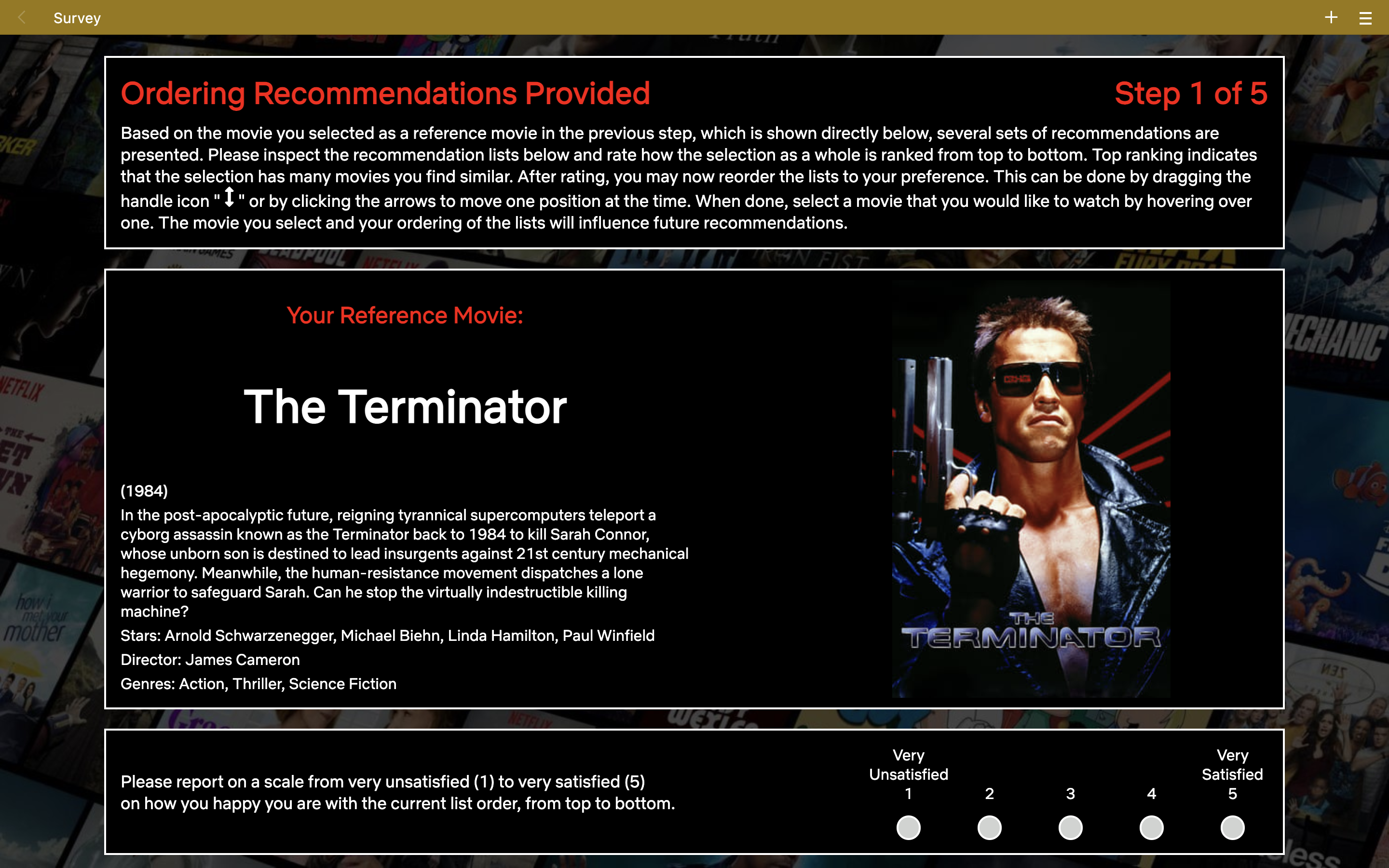
# Step Four
A user is asked to make changes in the order according to their preferences. A user has to choose a movie from one of the lists to proceed.

# Step Five
A user goes on to control their recommendations four more times.
# Step Six
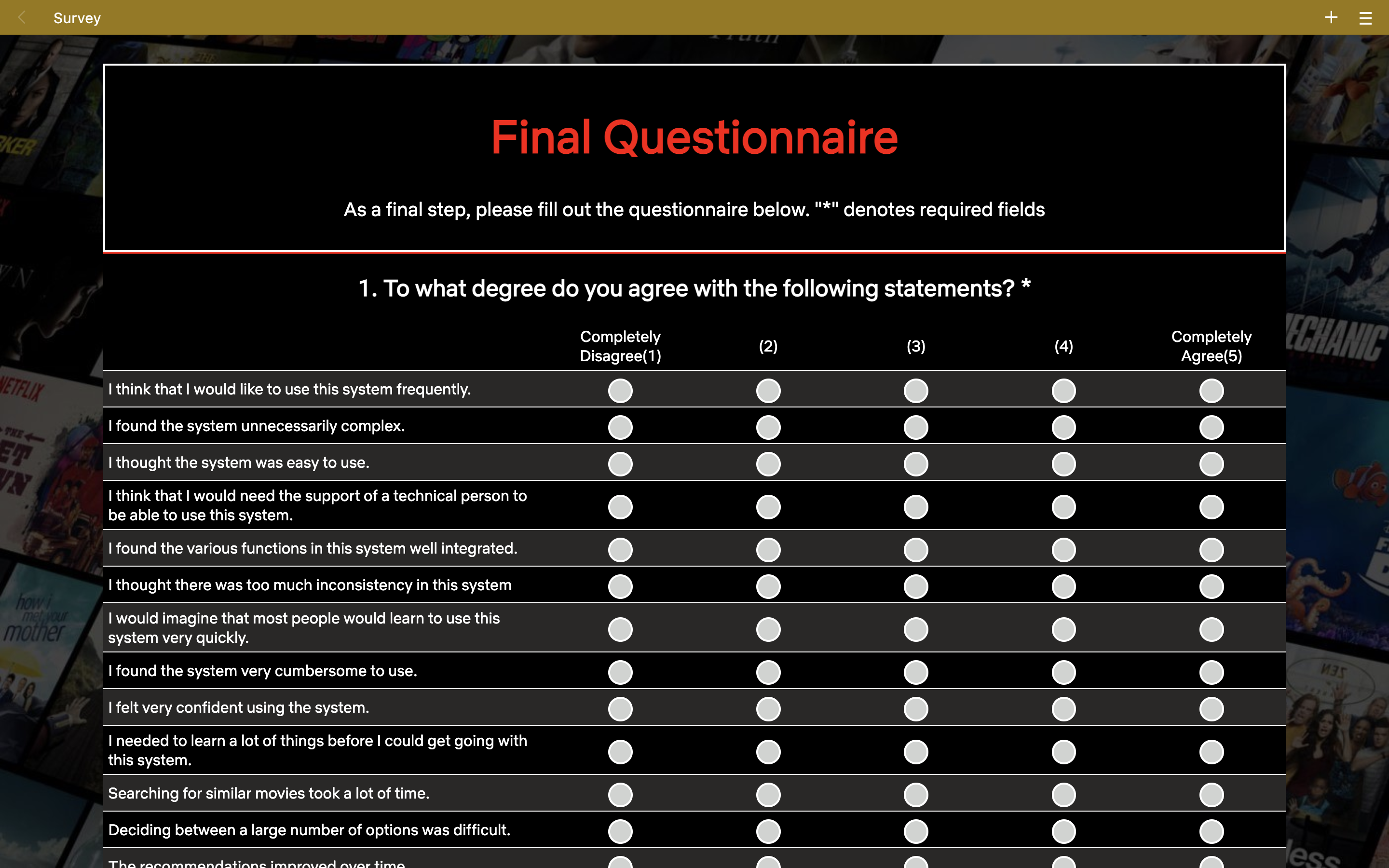
A user is asked to fill out the final questionnaire regarding their experience and demographics.